Chemical-looping combustion and chemical-looping with oxygen uncoupling for CO2 capture, covering oxygen carrier, reaction kinetics, CFD simulation, cold-flow model and hot rig
1. Introduction
Current state-of-the-art carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies usually have to overcome the problems of high energy penalty and capture cost, therefore, theoretical innovation and technological breakthroughs of CCS are necessary. Chemical looping combustion (CLC), which utilizes circulating solid oxygen carrier particles to transmit active oxygen from air reactor to fuel reactor, is regarded as one of the most promising CCS technologies. CLC exhibits the comprehensive advantage of high energy conversion efficiency, low cost for carbon capture and pollutant control.
2. Research findings
(1) Initiative design and conditioning efficiency of oxygen carrier
Oxygen carrier particles act as a bridge of the active oxygen transfer and energy transfer between the fuel reactor and air reactor. The optimization design and batch preparation of a high-performance oxygen carrier are the key factors for low cost and scaling-up of CLC systems. A lot of oxygen carriers, such as NiO/NiAl2O4, CuO/CuAl2O4, CuFe2O4, copper-decorated hematite and copper ore, etc., upon on initiative design, were developed and examined for oxygen carrier materials of CLC/CLOU and a spouted bed batch granulation method has been developed.
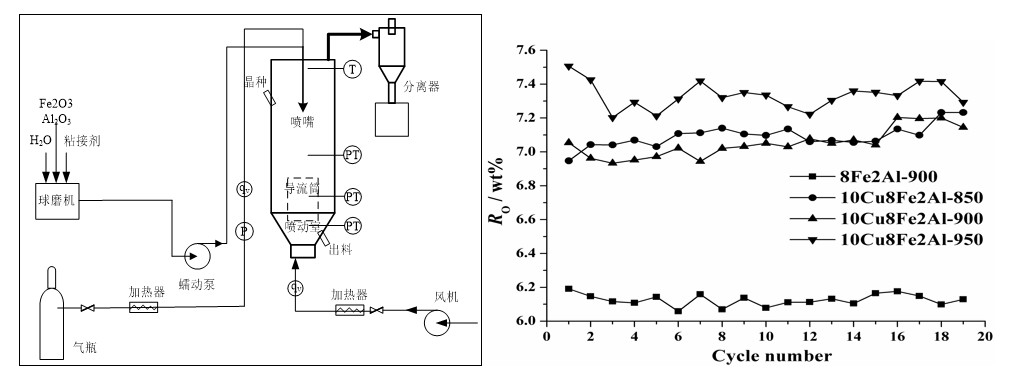
Granular process of batch spouted fluidized bed (left) and relations of copper modified Fe2O3/Al2O3 between oxygen carrier rate and number of recycles (right)
Reference
(2) Thermal-chemical characteristic of Chemical Looping Combustion/Chemical Looping with Oxygen Uncoupling Process (CLC/CLOU) with fuel such as coal etc.
Our studies focus on the following several aspects of coal-based CLC/CLOU:
A. Selection of typical oxygen carriers, including NiO/NiAl2O4, Fe2O3/Al2O3, CuO/CuAl2O4, CuFe2O4, natural ores (mainly iron ore and copper ore) and modified ores etc;
B. Reaction characteristics and cycling performance of these oxygen carriers with typical Chinese coals or the production of the coal gasification/pyrolysis;
C. Reaction mechanisms and kinetic behaviors of coal-based CLC/CLOU process.
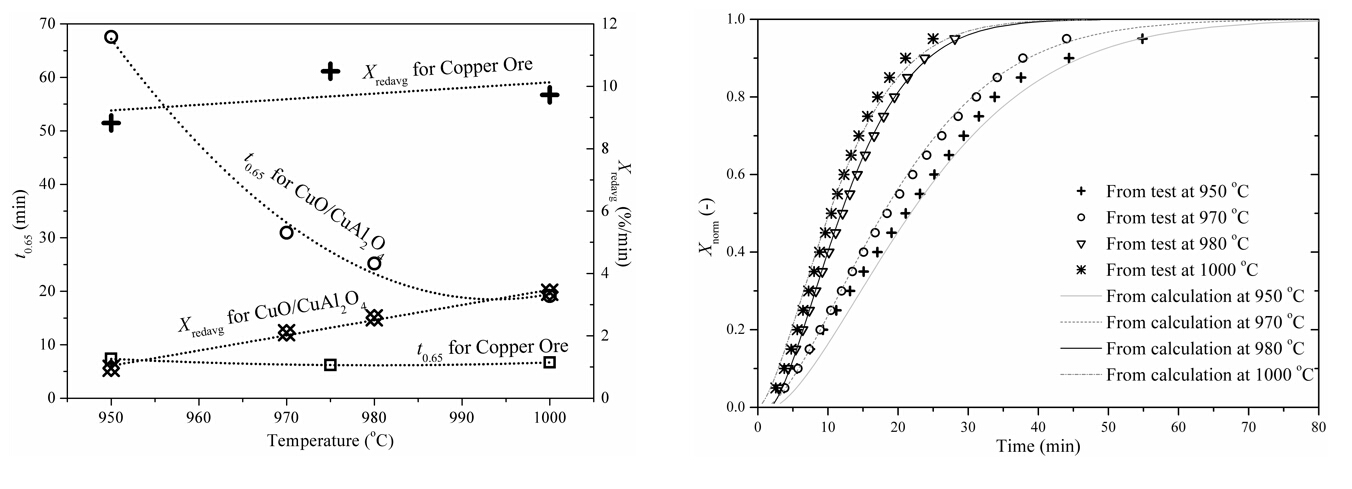
Chemical reaction characteristicof CuO/CuAl2O4 and natural copper ore coal-based chemical looping oxygen decoupled combustion (left) and oxygen release kinetics of CuO/CuAl2O4 oxygen carrier (right)
Reference
(3) Design and operation of Interconnected Fluidized Bed reactors for Chemical Looping Combustion
Interconnected fluidized bed reactors (5kWth, 50kWth) were designed and constructed. The fluid dynamic behaviors were investigated in terms of cold-model and hot-model experiemnts and the CFD numerical simulations. Some key factors (Combustion efficiency and CO2 capture efficiency, etc) in CLC/CLOU using different oxygen carriers and different fuels were measured, and suitable operation condition was obtained. The studies offer guidance to the system scaling-up and industrial application.
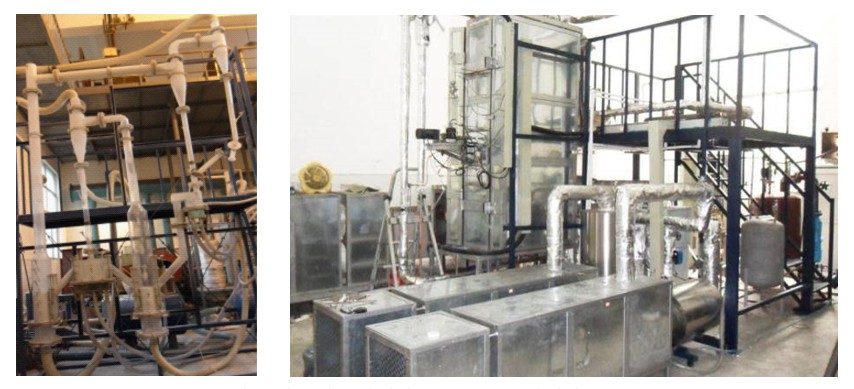
Cold bench (left) and hot bench (right) of serial fluidized bed
Reference
Address: hongshan district in wuhan city, hubei province no road 1037 yu hua zhongke
University of technology state key laboratory of coal combustion, room 214
Zip code: 430074
Telephone: 027-87542417
 Scan,can focus on
Scan,can focus onHubei hubei ICP for 05003321-1 42011102000123 male may be prepared
Powered by: StudyStone